CBC stands for Competency-Based Curriculum. This is the new education system in Kenya that is currently set to replace the 8-4-4 education system.
The system was introduced in 2017. The CBC was researched and developed
by KICD (Kenya Institute of
Curriculum Development). This new curriculum is here to stay as it had been
gradually introduced and is steadily replacing the 8-4-4 education cycle. At this
point in time, 8 (of the 8-4-4 cycle) consisting of 8 years of primary
education is being dismantled into a 6-year term. As such all and one need to
get acquainted with this new system.
This article gives a definitive guide on the new Competency-Based Curriculum
cycle that learners under its care will transition through to reach their careers. To
learn more its features click on Competency-Based Curriculum Features. As such it is essential to learn where we are
coming from, to where we have reached.
Kenya's Education System Cycle History
The Kenya education system started out with 7-4-2-3 system, a formal
education system introduced by the British Colonial rule in 1963. The education
cycle comprised of :
- 7
years in primary school
- 4
years in lower secondary school
- 2
years in upper secondary school
- 3
years(minimum) in university education
Then it was replaced by 8-4-4 system in 1985. Which consisted of:
- 8
years in primary school
- 4
years in secondary school
- 4
years(minimum) in university education
The new education system was introduced in 2017 with a 2-6-3-3-3 system
consisting of:
- 2
years in pre-primary education
- 6
years in primary education
- 3
years in junior secondary education
- 3
years in senior secondary education
- 3
years(minimum) in university education
CBC Education System
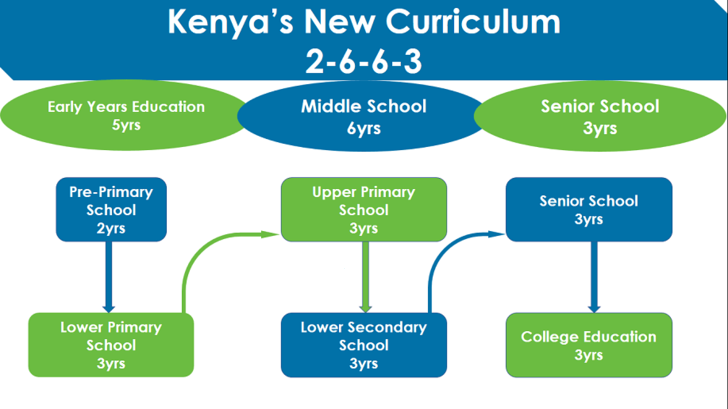
The Competency Based Curriculum (CBC) consist of 2-6-3-3-3 education cycle.
Every learner shall transition through a minimum of 17 levels, every level as
period of 1 year. The KICD has grouped them into 4 general categories:
- Early
Year Education (Pre-Primary & Lower Primary)
- Middle
School (Upper Primary & Lower Secondary)
- Senior
School (Upper Secondary)
- Tertiary
Education (TVET or University)
What used to be called Subjects are now known as Learning
Areas. Topics are known as Strands and Sub-topics called Sub-Strands.
Early Year Education (EYE)
This level bestows mastery of basic skills upon the learners. This group
consists of 2 sub-categories:
- Pre-Primary
- Lower
Primary
To find out more about the Learning Areas(Subjects) of this
group, continue reading below.
Pre-Primary
This first entry takes a period of 2 years, a learner enters the education system at the minimum age 4 of years old. The first class is PP1 short for Pre-Primary 1 followed by PP2 (Pre-Primary 2). This is what used to be referred to as Nursery. Prior to this entry level, the Day-Care also exists. It takes 1 year but is not a requirement.
Lower Primary
After Pre-Primary, the learner enters the Grade level. This consist of:
- Grade
1
- Grade
2
- Grade
3
In order to proceed to Middle School, the Kenya National Examination Council (KNEC)
will have learners sit an exam or rather assessment, this together with a
combination of class-based assessment shall determine if a learner is fit to
proceed to the next level.
Middle School
A learner at this level is said to be in Middle School, this consist of:
- Upper
Primary
- Lower
Secondary
Upper Primary
Consist of 3
- Grade
4
- Grade
5
- Grade
6
At the end of Grade 6, KNEC will have them sit for an
assessment, to determine the readiness for the Lower Secondary Level.
Lower Secondary
When learners has 3 levels, consisting of:
- Grade
7
- Grade
8
- Grade
9
At the end of Grade 9, KNEC will have them sit for an
assessment, to determine the readiness for the Senior School.
Senior School
At this stage, learners now start to specialize based on their career
choices. Time taken here, will enable them to see where they fit in their
career.
Careers are generally categorized into:
- Arts
& Sports Sciences
- Social
Sciences
- STEM
Based on the category the learner has decided, the learner
will transition in
- Grade
10
- Grade
11
- Grade
12
After this, the learner based on their career choices will
either attend a Technical and
Vocational Educational and Training (TVET) or University or can engage
in entrepreneurial business.
University education
If they choose tertiary education and training, they will undergo a minimum of 3
years. Some careers of cause require longer time frames.
The academic structure of the new curriculum
The new structure has three levels namely: early years, middle school, and
senior school.
Pre-Primary
This level takes two years – PP1 and PP2 each for a year.
Each learner is expected to begin with it. The subjects to be taught include
the following:
1. Language Activities
2. Mathematical Activities
3. Environmental Activities
4. Psycho-motor and Creative Activities
5. Religious Education Activities
Lower – Primary
After completion of Pre-Primary the learners will be promoted to Lower Primary
which is comprised of Grade 1 to Grade 3, hence, minimum of three academic
years will be spend. The subjects to taught include:
1. Literacy
2. Kiswahili Language Activities/Kenya Sign Language for deaf
3. English Language Activities
4. Indigenous Language Activities
5. Mathematical Activities
6. Environmental Activities
7. Hygiene and Nutrition Activities
8. Religious Education Activities
9. Movement and Creative Activities
Upper Primary
This include commonly known as Grade four, Grade five and Grade six. Hence will
take a minimum of three academic years. The subjects includes:
1. English or Kenya Sign Language (for learners who are deaf)
2. Home Science
3. Agriculture
4. Science and Technology
5. Mathematics
6. Religious Education (CRE/IRE/HRE)
7. Creative Arts
8. Physical and Health Education
9. Social Studies and optional Foreign Languages (Arabic, French, German,
Mandarin)
Lower – Secondary Education ( Junior school)
The next level after Upper Primary is Lower – Secondary. It comprises of Grade
7 to 9. Its is a lower category of secondary education (made up of Lower
Secondary (Junior school) and Upper Secondary (Senior School)).
This level will expose the learner to a broad based
curriculum to enable them to explore their own abilities,personality and
potential as a basis for choosing subjects according to career paths of
interest at the senior school. Learners will also undergo a rigorous career
guidance programme and be exposed to the related subjects to enable
them to make informed choices as they transit to senior school. Subjects will
be categorized core and optional groups.
Core group subjects
1. Kiswahili or Kenyan Sign Language for learners who are deaf
2. English
3. Mathematics
4. Integrated Science
5. Health Education
6. Pre-Technical and Pre-Career Education
7. Social Studies
8. Religious Education – which learners choose either Christian Religious
Education/Islamic Religious Education/Hindu Religious Education
9. Business Studies
10. Agriculture
11. Life Skills Education
12. Sports and Physical Education
Optional subjects
In this group learners will choose a minimum of one and a maximum of two
subjects according to personality, abilities, interests and career choices. The
group includes:
1. Visual Arts
2. Performing Arts
3. Home Science
4. Computer Science
5. Foreign Languages (German, French, Mandarin, Arabic)
6. Indigenous Languages
7. Kenyan Sign Language
Upper – Secondary
Also referred as Senior School. This will mark the end of Basic Education. It
will span a minimum of three academic years. The learner entering this level
shall have had opportunities at lower secondary to explore their own potential,
interests and personality and is therefore ready to begin specialization in a
career path of choice. The specialization entails choosing to pursue studies in
one of the three pathways available in senior school. He or she can choose the
Arts and Sports Science, Social Sciences or Science Technical Engineering and
Mathematics (STEM) pathway. Alongside a given pathway, it is expected that a
learner takes the two core subjects provided, irrespective of the pathway.
Arts and Sports Science Pathway
The Arts
Core subjects: Legal and Ethical issues in Arts, Communication Skills
Optional Subjects
The learner will be required to take one of the following subjects: Performing
Arts( Music, Dance, Theatre and Elocution) and Visual and Applied Arts(Fine
Art, Applied Art, Time Based Media, Crafts)
Sports Science
Core subjects: Human Physiology, Anatomy and Nutrition, Sports Ethics
Optional Subjects
The learner shall choose a minimum of one and a maximum of two of the
following subjects according to the learner’s personality, interests, ability
and career choices: Ball Games, Athletics, Indoor Games, Gymnastics, Water Sport,
Boxing, Martial Arts, Outdoor Pursuits, and Advanced Physical Education.
The Social Sciences Pathway
The learner is expected to choose a combination of subjects in line with their
career choices. The learner will choose a minimum of three and a maximum of
five subjects.
Humanities: History and Citizenship,
Geography,Christian Religious Education/ Islamic Religious Education/Hindu
Religious Education, Business Studies, and Mathematics
Languages: English Language, Literature
in English, Lugha ya Kiswahili, Fasihi ya Kiswahili, Kenyan Sign
Language,Indigenous, Languages, Arabic, French, German, and Mandarin.
Note: Business Studies can be taken along with languages.
The Science, Technology, Engineering and Mathematics
Pathway
The Science, Technology, Engineering and Mathematics (STEM) pathway shall be
offered in 60% of senior schools. It will therefore take 60% of the students
entering senior school from lower secondary and it shall comprise four career
tracks.
Pure Sciences
Core subjects: Community Service Learning, Physical Education, and ICT.
Optional
The learner will select a minimum of three of the following subjects:
Mathematics, Physics, Chemistry, and Biology.
Applied Sciences
Core Subjects: Community Service Learning, Physical Education, and ICT.
Optional
The learner shall in addition select one of the following subjects:
Agriculture, Computer Science, Foods and Nutrition, and Home Management.
Technical and Engineering
Core Subjects: Community Service Learning, Physical Education, ICT,
Mathematics, Physics/Physical Sciences, Chemistry/Biology/Biological Sciences
Optional
The learner shall in addition select one of the following subjects:
Agricultural Technology, Geosciences Technology, Marine and Fisheries
Technology, Aviation Technology, Wood Technology, Electrical Technology, Metal
Technology, Power Mechanics, Clothing Technology, Construction Technology,
Media Technology, Electronics Technology, Manufacturing Technology, and
Mechatronics.
Career and Technology Studies (CTS)
Core Subjects: Community Service Learning, Physical Education, ICT
Optional
The learner shall in addition select one of the following subjects:
Garment Making and Interior Design, Leather Work, Culinary Arts, Hair Dressing
and Beauty Therapy, Plumbing and Ceramics, Welding and Fabrication, Tourism and
Travel, Air Conditioning and Refrigeration Animal Keeping, Exterior Design and
Landscaping, Building Construction, Photography, Graphic Designing and
Animation, Food and Beverage, Motor Vehicle Mechanics, Carpentry and Joinery,
Fire Fighting, Metalwork, Electricity, Land Surveying,science Laboratory Technology,
Electronics, Printing Technology, and Crop Production.
Education for Learners with Special Educational Needs
Learners with special educational needs, like any other learner, have potential
that needs to be nurtured. The special needs education curriculum model
outlined below indicates curriculum provision for learners with special
needs.Curriculum provisions for learners with special needs shall be in two (2)
modalities.
Learners with Special Needs Who Follow the Regular
Curriculum
The following learners may follow the same curriculum as learners without
identified with special needs.
1. Visual Impairment
2. Hearing Impairment
3. Physical Handicap
4. Mild Cerebral Palsy
5. Learning Disabilities
6. Autism
7. Communication Disorder
8. Gifted and Talented
9. Emotional and Behavioral Difficulties
Learners with Special Needs Who May Not have their needs
met from just following the Regular Curriculum
1. Mental Handicap
2. Deaf blindness
3. Severe Autism
4. Severe Cerebral Palsy
5. Multiple Handicaps
6. Profound Disabilities
Note: Digital literacy and pertinent and
contemporary issues will be integrated across all Subjects in all levels
Sample Competency-Based Curriculum Scheme of Work
The new Competency Based Curriculum (CBC) Scheme of Work is
structured according to the following categories: Week, Lesson, Strands,
Sub-Strands, Specific Learning Outcomes, Key Inquiry Questions, Learning Experiences,
Learning Resources, Assessment and Reflection. The following Table is a sample
template for the CBC scheme of work currently being used in Kenya under the new
2-6-3-3-3 System of Education.
|
Wk |
Lesson |
Strands |
Sub- |
Specific |
Inquiry |
Learning |
L. |
Asse- |
Refle- |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Conclusion
In this system learners will not sit for exams but they will be evaluated through Continuous Assessment Tests (CATs) on the skills acquired as opposed to cramming for exams as has been the case. The 2-6-3-3-3 model places emphasis on formative years of learning where learners will spend a total of 17 years. At Grade 4, learners will be introduced to the optional subjects offered at upper primary so as to make informed choices at Grade 7. Junior Secondary (grades 7, 8 and 9) and Senior Secondary Education (grades 10,11 and 12) will each take three years. Learners at senior secondary (ages 15-17) will focus on three areas of specialization depending on their skills, talents and interests. Graduates from this level will have the option to join vocational training centres or pursue university education for three years.The curriculum was piloted in 2017 between May and September across 470 schools, 10 in each county. Its actual implementation started in January, 2018. The implementation covered pre-school and Grade One, Two and Grade three. Grades above will be implemented gradually. 8-4-4 will continue until the last batch sits Form Four exams in 2026. Therefore, Kenya Certificate of Primary Education (KCPE) and Kenya Certificate of Secondary Education (KCSE) exams will continue until the new system runs its complete cycle.